The banking system plays a vital role in economic development and is one of the most significant components of the financial system of any country. The banks not only facilitates the creation of credit but at the same time they provide numerous other services for the management and transactions of funds between two persons or entities.
In this article, we will help you to understand what exactly the banks are? what are the key functions they perform and how important they are for the economic development of a country?
You’ll be able understand the following topics by the end of this article.
- Banks Definition
- Primary Functions of Banks
- Secondary Functions of Banks
- Types of Deposits
- Agency functions of banks
- General Utility functions of banks
Table of Contents
Banks Definition:
The banks refer to those financial intermediaries/ institutions which functions under the supervision of the Central Bank (Reserve Bank of India) accepting deposits from the general public or business entities and granting loans and advance to other businesses or individuals.
The banks act as an intermediary between the people having surplus funds and people with deficit funds. The Banks accept deposits from the individuals or businesses who have excess/ surplus funds and avail loan/ advance to the businesses or people with deficit funds who require money. They not only ensure the guarantee of payment on demand but also provides the rate of interest on the deposited amount.
Thus we can say that the banks are the financial institutions which regulates supply of money from surplus to deficit areas and hence control inflation rate in the financial system of the countries.
Now let us understand the major other functions of banks in details.
Functions of Banks:
There are basically two categories of services which are performed by the banks.
- Primary Functions of Banks
- Secondary Functions of Banks
1) Primary Functions of Banks:
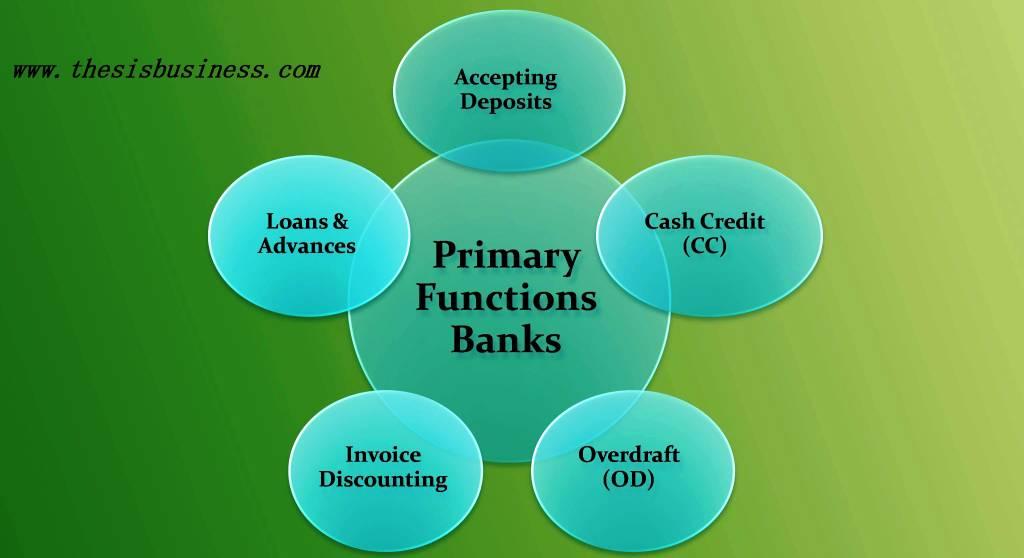
All banks perform two primary functions as follows.
- Accepting Deposits
- Avail Loan and Advances
Accepting Deposits:
All banks primarily accept deposits from general public and businesses as we know, however, there are various types of deposits in which form of the banks gather funds from the public or entities.
- Saving or demand deposits: The saving deposits also known as demand deposits are the popular and simplest form of deposits encourages savings. It offers a nominal interest rate and guarantees on-demand payment whenever the customers ask. However, there is a standard of minimum account balance which has to be fulfilled.
- Fixed or Time deposits: The fixed deposits also known as time/ term deposits refers to a deposit of specific amount for the stipulated period of time at a predetermined rate of interest. The depositor can’t withdraw his funds till the completion of the maturity period.
- Recurring Deposits: The recurring deposits (RD) are a special account in which the depositor has to deposit money at regular intervals such as monthly, quarterly or weekly for a stipulated time period. The main features of the RD account are that it offers fixed interest rate same as fixed deposits.
- Current Deposits: The current deposits/ account are typically used by companies/ firms to facilitate business transactions. In the current account, there are no limitations on the number of transactions performed by the business firms, however, such deposits don’t provide any rate of interest as well. The current accounts are frequently used by the businesses for receiving and doing payments among various parties.
Avail Loan & Advances:
The funds collected from the depositors through a different form of deposits are allocated among various businesses and individuals in form of loans/ advances. The banks charge a comparatively higher rate of interest on loans/ advances. The banks typically offer the following types of loans or advances to the business enterprises or public.
- Cash Credit (CC) Facility: The banks provide cash credit facilities to the businesses against collateral such as tangible assets, inventory or machinery etc. Cash credit (CC) is a short term loan offered by the banks and the interest is charged on excessive/ surplus withdrawal of funds on monthly basis over a certain limit. The CC loans are generally provided to the customers of banks, however, it sometimes offered to non-customers as well in certain scenarios.
- Overdraft Facilities (OD): The Bank provides overdraft (OD) facility to their current account holders against security. Overdraft account provides the facility of withdrawal of extra funds but up to granted limit and interest payable on such surplus withdrawal of money.
- Bill/ Invoice Discounting: The banks also provide short term advances to the businesses/ firms in form of Bill discounting. The bill/ invoice discounting is nothing but an advance against the company’s receivable (due payments) before the maturity date. In simple words, the companies keep their invoices as collateral with the banks to get money less than the actual value of bills. The amount granted by the banks generally depends on the maturity period of bills and creditworthiness of the buyers.
- Loans: The banks also provide medium and long term loans to individuals which can be secured or unsecured. Some examples of secured loans are home loan, vehicle loan, gold loan etc whereas an example of unsecured loan is personal loans which are typically provided on the higher interest rate. The duration of such loans is predetermined repayment can be done in monthly instalments.
2) Secondary Functions of Bank:

In addition to primary functions, banks also perform other important functions on the behalf of their customers as well as government entities called secondary functions of banks. It can be classified into two parts.
- Agency Functions
- Utility Functions
Agency Functions of Banks:
The bank acts as an intermediary between its customers and government/ business entities. Hence they work as an agent for their customers to pay bills, collection of payments etc. Some agency functions of the bank are as follows.
- Periodic Payments: The banks do periodic payment such as electricity bills, water bills, insurance premium, monthly instalments, school fees etc on behalf of their customers. Such regular payment is debited at a fixed date from the customer’s account automatically to reduce the burden of the customers.
- Periodic Collection: The banks also receive periodic payments on behalf of their clients such as public entities, corporations or businesses. The banks play a vital role in the collection of payment from huge audiences. For instance salary, pension, collection of fees or security deposit for government entities etc.
- Fund Transfer: The banks facilitate the transfer of funds from one person/ party to another person/ party and from one city to another city using NEFT, RTGS, IMPS etc.
- Cheques Negotiation: The banks act as a clearinghouse agent between two parties for the clearance of the cheque. These days cheque’s payment is preferred, safe mode of payment among businesses. Hence cheque negotiation is one of the major functions of banks.
- Portfolio Management: The banks also facilitate stock market investments and trading through portfolio management. The money is debited and credited directly in the customer’s account while trading in the stock market. Thus banks help individuals to build their portfolio by purchasing stocks, debentures, mutual funds or other securities.
- Advisory Services: The banks sometimes act as trustee, advisor or representative for their high profile clients. Such services are typically provided by banks in case of foreign deals or other high-value affairs.
Utility Functions of bank:
In addition to agency functions, banks perform some other general utility functions as well. Such popular services offered by banks are as follows.
- Issuance of Bankers Cheque, demand drafts, letter of credit, bank guarantee to facilitate the businesses as well as the public.
- Bank provide locker services for valuable property/ documents of the customers.
- Sometimes banks provide underwriting services on behalf of their customers for the purpose of fundraising from the public through its merchant banking dividend.
- The banks also deal with foreign exchange to facilitate cross border transactions during international trade.
- Public welfare programs: The banks also help in the implementation of various government schemes and participate in different social activities, literacy and awareness campaigns.
- Other Utility Functions: The banks help you to pay electricity bills, receiving the gas subsidy, house taxes, insurance premium, KCC loans, pension and AEPS (Aadhar Enabled Payment Service) withdrawal in remote areas.
Wrapping Up:
Hope you have understood the significance of banks in the financial system of a country. The banks stabilise the rate of inflation in the economy by controlling the supply of funds.
In a nutshell, banks established a bridge between the community of surplus and deficit funds so that money could be utilised by the community who require it and at the same time, people having surplus funds would earn some interest over their savings.
Recommended Articles:
- 5 Major Functions of Commercial Banks
- Indian Banking System
- History of Banking in India
- Nationalization of Banking in India
References: Byjus.com Functions of Banks (source)
