The Central Bank is the Apex institution of a country whereas commercial banks are a minor unit of the whole financial system. Although both central bank of a country and commercial banks are the backbone of the financial system of any country because it mobilises funds, creates credit, regulates the supply of funds and hence controls the rate of inflation in the economy.
This article will explain the key difference between central bank and commercial bank.
Table of Contents
Central Bank vs Commercial Bank (Comparison Chart):
To understand the difference between the central bank and commercial banks quickly, see the following comparison table so that you can get a quick overview regarding this lesson.
| Aspects | Central Bank | Commercial Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The Apex (Statutory) body, being a monetary authority, control supply of money and inflation rate and other significant financial affairs in the country. | The financial institution which acts as an intermediary between debtors and creditors to establish financial stability in the economy by accepting deposits and advancing debt. |
| Governed By | Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 | Banking Regulation Act, 1949 |
| Identity | Government's Bank | Bank for citizens and corporates |
| Body | Government Body | Public or Private entity |
| Objective | Public welfare and economic development in the country | Earn Profits |
| Lend to | Financial institutions and Government | Individuals and corporates |
| Other Functions | Issuing, printing, circulating Currency notes | NO |
| Monetary and Other policies | Formulates and implements | Follow the policies made by central bank |
| Foreign Exchange Reserve | Custodian of Foreign currency | Dealer of Foreign currency |
| Deal with | Government | Citizens and business entities |
| Existence | Only One | Many |
Also, see the following hierarchy of the Indian financial system to understand the position of commercial banks.
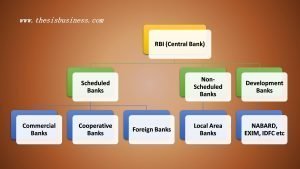
Central Bank & Commercial Bank:
The central bank and commercial bank are equally significant for the economy of any country, however, their functions are different from each other. For instance, Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of India whereas State Bank of India (SBI), ICICI Bank, Punjab National Bank (PNB) etc are the commercial banks. We can distinguish between the central bank and commercial bank based on their functions and different aspects.
The Central bank of a country ie. Reserve Bank (in case of India) is the Statutory body/ supreme authority of financial institutions and also known as Government’s bank. The central bank is responsible to formulate and implement the fiscal and monetary measures on the behalf of Government in the country.
On the other hand, commercial banks accept deposits, avail loan or advances, deals in foreign exchange and provide other digital and core banking services to the general public and business entities. In fact, commercial banks act as an intermediary between borrowers and lenders to mobilize the funds from those who possess excess funds to those who require funds.
In other words, the central bank is the banker’s bank ie. head of all scheduled (commercial and cooperative bank), non-scheduled and NBFCs (Non-banking finance company) or we can say the central bank regulates the commercial banks and other financial institutions in the country.
Functions of Central Bank and Commercial banks:
The major differences between the central bank and commercial banks lie in their functions. In India, Reserve Bank is the central bank and established as per the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The central bank or Apex Bank performs the following functions.
- Issuing, printing and circulation of currency notes.
- Licensing of different financial institutions in the country
- Formulates and implements monetary policies
- Control flow of funds in the economy
- Custodian of Foreign exchange reserves
- Operates payment and settlement system
- Appoints chairman of Commercial banks.
- The central bank also avails finance for financial institutions like commercial banks, cooperative banks, RRBs etc at repo rate or bank rate.
For more details follow: 10 Major functions of RBI
On the other hand, the major functions of commercial banks are as follows.
- The commercial banks create and allocate credits.
- Open and operates different accounts like saving accounts, current accounts, overdraft accounts, RD accounts etc of the general public or enterprise.
- Provide other banking services like credit cards, debit cards, mobile banking, negotiation of cheques ATM etc.
- Provide various type of loans such as Gold loan, personal loan, vehicle loan, home loan etc.
- Deals in foreign exchange.
- Issue letter of credit and discount bill of exchange
for detailed information follow the link: 5 Major functions of commercial banks
Hope you have understood the basic functions of commercial banks and central bank. Thus we can easily understand how the functions central bank differs from the commercial banks.
Difference Between Central Bank and Commercial Bank:
Now let me compare head to head difference between commercial banks and central bank based on other aspects as well.
- The central bank of India (Reserve Bank) is established and operate as per the RBI Act, 1934 on the other hand, commercial banks are regulated under the Banking Regulation Act 1949.
- The central bank (RBI) is the Government’s bank represents the bank of Indian Government in IMF and World Bank whereas commercial banks are for individuals and business enterprises.
- The central bank is the government body whereas commercial banks may be the public or private entity.
- The main objective of the central bank is economic development and public welfare of the country, on the other hand, the objective of commercial banks is to make profits.
- The central bank issue, print, circulate the currency notes whereas commercial banks don’t perform such functions.
- The central bank avail funds for the commercial banks and other financial institutions itself at repo rate and bank rate, on the other hand, commercial banks provide loans for individuals and corporates.
- The central bank, being a monetary authority, formulates and implements monetary policies to stabilize the rate of inflation in the economy whereas commercial banks follow the guidelines issued by the central bank.
- The central bank itself regulates and supervises the payment and settlement system (like NEFT, RTGS, bank transfer) performed among several commercial banks and other financial institutions whereas commercial banks only request to settle the transactions.
- The central bank is the custodian of foreign exchange reserves whereas the commercial banks are the dealer of foreign currency.
- The central bank deal with the government and financial affairs, on the other hand, commercial banks deal with citizens and business entities in the country.
- There can be only one central bank whereas the commercial banks may be as many as they can have in the country.
Conclusion:
Hope you would have understood most of the major differences between the central bank and commercial banks. Still, in a nutshell, we can conclude the above article in the following points to easily remember their differences.
- The central bank is the apex body of the whole financial institutions in the country and commercial banks are simply those financial institutions which accept deposits and provide loans and other banking services to the individuals and enterprises.
- The central bank formulates several guidelines and policies to regulate and supervise the commercial banks and other financial institutions whereas commercial banks have to follow the guidelines made by the central bank.
- The central bank doesn’t deal with the general public or enterprises, on the other hand, commercial banks deal with the general public and business entities.
Recommended Articles:
Difference between Scheduled and Non-scheduled Banks
References:
