Although Commercial banks and cooperative banks are included under the category of scheduled banks, yet there is the key difference between commercial and cooperative bank. The main objective of commercial banks is to make profits, however, cooperative banks function on the principle of cooperation, self-help or mutual help of its members such as farmers, small scale businesses, street vendors etc especially in rural, semi-urban or urban locale.
Therefore, in this lesson, we will discuss the key difference between cooperative banks and commercial banks. But before we go-ahead let us understand the basic structure of the banking system in India.
Table of Contents
Commercial Banks and Cooperative Banks:
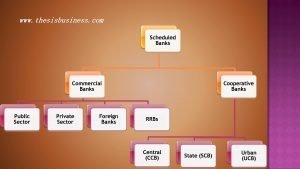
The commercial banks are the financial institutions which are authorised to receive deposits from public, industries and commerce as well as cater short, medium and long term requirements of individuals, entrepreneurs and corporates in form of different types of loans/ advances. In addition, commercial banks also provide various other banking services like internet banking, debit card, credit card, money transfer, foreign exchange, bill discounting, letter of credit etc.
There are basically four categories of commercial bank functioning in India:
- Public Sector Banks (Nationalised Banks)
- Private Sector Banks
- Regional Rural Banks
- Foreign Banks
On the other hand, cooperative banks are the cooperative societies registered under the Cooperative Society Act, 1965 of the concerned state. The cooperative banks function on No profit No loss basis, that means their main objective, as discussed above, are to help backward segment of the society like agriculturists, labours, small vendors, self-employed. The cooperative banks accept deposits from its members and fulfil short term needs of those where the banking services are still unavailable or those who are unable to get regular banking services.
The cooperative banks are basically three types:
- Urban Cooperative Banks
- State Cooperative Banks
- Central Cooperative Banks
The Urban Cooperative Banks are situated typically in rural areas or remote area cater to the financial needs of its locale, however, State Cooperative banks function in the semi-urban or urban areas and responsible for supervising and auditing the working procedure and also provide credit facility to UCBs. The Central Cooperative Banks are the Apex banks of all cooperative banks, basically operate in the metro cities and responsible for auditing, supervising and availing the credit facilities to its subordinate banks (UCBs & SCBs).
See Also, Difference between Commercial banks and Central Bank
Difference Between Commercial and Cooperative Bank:
The following comparison table contains every aspect based on which commercial banks and cooperative banks can be distinguished quickly.
ASPECTS OF COMPARISON COMMERCIAL BANKS COOPERATIVE BANKS
Incorporation Banking Regulation Act, 1949 Cooperative Society Act, 1965
Main Objective Earn Profits Provide Banking Services
Types of Entity Private and Public Private
Rate of Interest Low High
Scope of Operation Larger Scale Limited Scale
Voting Rights NO YES
Reserve Policy Strictly maintains CRR and SLR Comparatively less strict
Governing Body Reserve Bank of India RBI and Registrar of Cooperative Society
Non Performing Asset High Low
Merchant Banking Service YES NO
Mutual Fund YES NO
Bill Discounting and Letter of Credit YES NO
Foreign Exchange Services YES NO
Commercial Banks vs Cooperative Banks:
Now let us conduct a point to point comparison between cooperative banks and commercial banks. We can differential cooperative banks from commercial banks based on the following perspectives.
1) Incorporation:
The commercial banks are registered under the Banking Regulation Act 1949, on the other hand, cooperative banks are incorporated under the Cooperative Society Act, 1965 of the respective states.
2) Primary Objective:
The primary objective of commercial banks is to maximize profits whereas the main objective of cooperative banks is to provide credit facility to the poor/scheduled/backward people in society.
3) Types of Entity:
The commercial bank can be either private or public entity, however, cooperative banks can be a private entity only.
4) Rate of Interest:
The rates of interest are comparatively higher in case of cooperative banks whereas commercial banks offer lower interest rates.
5) Scope of Operation:
The commercial banks function at a larger scale and can even function in abroad, on the other hand, cooperative banks operate at a small scale and their operation can be limited to the district level as well.
6) Voting Rights:
The members or beneficiary or borrower of cooperative banks possess the voting rights through which they can influence the lending policies of the banks. Contrary, the borrower/ customer of commercial banks are an account holder of the bank who doesn’t have such voting right to influence the lending policy of commercial banks.
7) Reserve Policy (CRR & SLR):
Although both cooperative banks and commercial banks have to maintain the cash reserve ratio (CRR) and statutory liquidity ratio (SLR), yet the strictness to follow CRR and SLR for cooperative banks is less than the commercial banks.
8) Governing Body:
Although commercial banks and cooperative banks both are governed by the Reserve Bank, the central bank of India, yet the commercial banks are under the control of the Reserve Bank directly, however, cooperative banks have to follow the guidelines made by both Registrar of Cooperative Society as well as RBI.
9) Non Performing Assets:
The non-performing asset (NPA) is higher when it comes to commercial banks whereas in case of cooperative banks NPA is comparatively less.
10) Other Major Services:
Commercial banks and cooperative banks can also be distinguished based on their offered services. Some major differences are explained below.
- Merchant Banking Services: Commercial banks also offer merchant banking services whereas cooperative banks don’t offer such services
- Mutual Funds: Commercial banks or their subsidiary also offer SIP/ mutual funds service to their customers but cooperative banks don’t.
- Bill Discounting and Letter of Credit: Commercial bank or it’s subsidiary also offers invoice discounting and L/C facilities to manufacture or supplier while the cooperative bank doesn’t provide such services.
- Foreign Exchange Services: Commercial banks may also provide foreign exchange services, on the other hand, cooperative banks don’t provide such kind of services.
Conclusion:
This article has covered all significant difference between commercial and cooperative banks, hope you will be able to understand these key differences. In a nutshell, we can conclude the above lesson within three important points.
- Commercial banks are joint-stock banks (public or private) regulated under the Banking Regulation Act 1949 while cooperative banks of cooperative societies registered under the Cooperative Society Act 1965.
- Commercial banks are operated with higher funds and larger extents, on the other hand, cooperative banks function with fewer funds and at limited extents.
- Commercial banks provide a variety of services to individuals, trade and corporates and the main objective is to earn profits whereas cooperative banks provide limited services as compared to commercial banks to mainly farmer, labour and small businessmen.
Related Articles:
Difference between Scheduled and Non-scheduled Banks
Difference between CRR and SLR
Cooperative Banking in India | An Overview
5 Major functions of Commercial Banks
References- Slideshare
