Indian Banking System is broadly classified into three categories: Scheduled Banks, Non-scheduled Banks and Development Banks. In this lesson, we will discuss the difference between scheduled and non-scheduled banks.
The banks are those financial institutions which accept deposits from the general public and corporations, avail advances/ loans to those who require funds and provide other banking services. There are various functions performed by the banks to facilitate the public as well as business enterprises/ corporations in India. The banks are one of the significant components of the Indian financial system.
See the following hierarchy to understand the structure of the banking system in India.
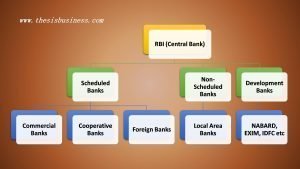
The Reserve Bank (RBI), being the Central (Apex bank) of India regulates and supervises the banking system in the country.
Table of Contents
Scheduled and Non-scheduled Banks:
In India, there are two major categories of banks: Scheduled bank and non scheduled banks.
As per Section 2 (e) of Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, the scheduled banks are defined as the financial institutions/ banks which are listed in the 2nd Schedule of Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. In other words, the banks which adhere to various ordinances, monetary policies and guidelines formulated by the Reserve Bank is known as scheduled banks.
Criteria to be listed in the 2nd Schedule of RBI Act:
- The Paid-up capital of any bank should not be less than 5 Lakhs.
- As per Section 42 of RBI Act, 1934, Every bank listed in 2nd Schedule are required to maintain the cash reserve with the Reserve Bank on a daily basis.
- The banks should not be involved in any activities due to which funds/ money /interest of the depositors is affected.
Advantages of being listed in the 2nd Schedule of RBI Act:
Every bank listed in 2nd schedule of RBI Act, 1934 are entitled to the following benefits.
- Every scheduled bank is eligible to get advance/ loan/ debt from the Reserve Bank at Bank Rate.
- The Reserve Bank rediscounts the bill of exchange of Scheduled banks considering as the first-class bill of exchange.
- The scheduled banks maintain cash reserve ratio with the RBI to avoid cash crunch and to ensure the solvency of banks.
Example of Scheduled Banks:
The scheduled banks can be categorized in the following groups.
- State Cooperative Banks
- Urban Cooperative Banks
- State Bank of India (SBI) and Associates
- Nationalised Banks
- Other Public Sector Bank (IDBI)
- Private Sector Banks
- Foreign Banks
To see the complete list of scheduled banks follow the link: Second schedule of Reserve bank of India Act, 1934.
On the other hand, Non-scheduled banks are those banks which are excluded from 2nd Schedule of RBI Act, 1934 and don’t follow the guidelines or rules and regulations laid by the RBI.
Non-scheduled banks don’t need to comply with the guidelines of RBI, however, they maintain the cash reserve with themselves but it is not a compulsion by the Reserve Bank.
Non-scheduled banks also not eligible to obtain advances/ debt from the RBI.
Scheduled banks vs Non-Scheduled banks:
| Basis of Comparison | Scheduled banks | Non-Scheduled banks |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning & Definition | The banks included in 2nd Schedule of RBI Act, 1934 are called Scheduled banks. | The banks which are not included in 2nd Schedule of RBI Act, 1934 are called Non-Scheduled banks. |
| Adhere to RBI Guidelines | YES | NO |
| Maintain Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) | With the Reserve Bank | With themselves |
| Advance/ debt from RBI | Eligible | Not Eligible |
| Member of Clearing House | YES | NO |
Difference between scheduled and non-scheduled banks:
Now let us discuss the head to head difference between scheduled banks and non scheduled banks.
- Scheduled banks always require to follow the ordinance or guidelines or monetary policies formulated by the Reserve Bank, on the other hand, non-scheduled banks don’t need to follow the guidelines prescribed by the RBI.
- Scheduled banks are listed in 2nd Schedule of RBI Act, 1934 whereas Non-scheduled banks are not.
- Scheduled Banks are entitled to obtain debt/ loan from the Reserve Bank, on the other hand, non-scheduled banks are not eligible.
- Scheduled banks can be a member of the clearinghouse whereas non-scheduled banks are not.
- All Scheduled banks maintain cash reserve ratio with RBI while non-scheduled banks maintain cash reserve ratio (CRR) with themselves.
Conclusion:
Hope you have understood the difference between scheduled and non-scheduled banks. In a nutshell, there are three points to remember when it comes to scheduled and non scheduled banks.
- The banks listed in 2nd Schedule of RBI Act, 1934 is scheduled banks and others are non-scheduled banks.
- Scheduled banks are eligible to take loans from RBI while non-scheduled banks are not.
- Scheduled banks maintain CRR with the Reserve bank whereas non-scheduled bank maintains CRR with themselves.
Recommended Articles:
Indian Banking System | Structure of Banking in India
Nationalisation of Banks in India
References:
jagranjosh.com, Reserve bank of India
