In this article, we will learn about the Bill of Exchange, its usage and features. We are going to discuss the following topics.
- What is Bill of Exchange? Meaning and definition.
- Features of Bill of Exchange
- Types of Bill of Exchange
- Participants in Bill of Exchange
- With Example
Table of Contents
What is Bill of Exchange?
“The Bill of Exchange is a written financial document/ instrument which promises an unconditional payment of the specific amount on a future specific date to the bearer of that financial instrument drawn by the creditor/drawer.”
Bill of Exchange (BOE) is frequently used international trade (export-import businesses) where unknown buyers and suppliers trade between themselves and goods or services are sold on a credit basis as well. In other words, its works just like post-dated cheques in local trade. However, it is replaced by the Paper Currency and Bank Wire nowadays.
The bill of exchange is further transferable by the endorsement to another party before the date of maturity also there is no interest payable by the debtor before the due date however interest might be applicable after the maturity date if this condition is mentioned in the bill of exchange.
Features of Bill of Exchange:
- A bill of exchange is a written document signed by both seller and buyer.
- It possesses detailed descriptions about quantity and price of traded material, date of maturity/ due date, name of the debtor, total amount payable.
- It is an unconditional order means there is no condition regarding payment at the date of maturity or due date. In other words, the debtor can not deny paying the amount mentioned in the bill of exchange to the bearer of this BOE.
- Bill of exchange is written/ drawn by the creditor/ supplier/ exporter and duly signed by both the parties.
- The terms and conditions are also accepted by the debtor/ importer/ buyer.
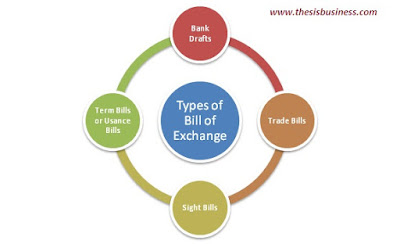
Types of Bill of Exchange:
A bill of exchange can be classified on the basis of issuing parties and the due date.
- If the bill of exchange is issued by the banks, it is known as a Bank Draft.
- On the other hand, if it is issued by an individual or a company, it will be known as Trade Bills.
- If the payment has to be done either immediately after certain conditions or activity like shipping or receiving of product or on-demand, such kind of Bill of exchange is known as Sight Bills.
- If the creditor/ supplier or exporter is ready to provide deferment to pay the bills such as 60 days, 90 days, in this case, is called Term Bills or Usance Bills.
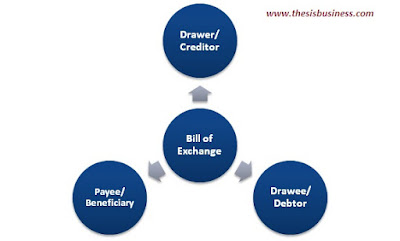
Participants in Bill of Exchange:
There are mainly three parties involved in a bill of exchange.
1) Drawer:
The drawer is an individual or company who issue/ write the bill of exchange.
2) Drawee:
Drawee is the debtor/ buyer who is under obligation to pay the mentioned amount in a bill of exchange.
3) Payee:
A payee is a company or an individual who is actually receiving the said amount by the debtor/ buyer.
Now let us discuss the above theory with an example.
Example:
Suppose a company ABC Ltd (in India) purchases some goods worth $ 10,000 from a supplier XYZ Pvt Ltd based at the United States. The supplier agrees to provide deferment of payment up to 90 days from the date of shipping.
Now the company XYZ Pvt Ltd draws a bill of exchange of $10,000 which is payable by the buyer/ debtor (ABC Ltd) on the due date (90 days from the date of shipping) say 01/02/2020. Further, the bill of exchange will be duly signed by both the parties.
Now suppose there is another party Mr P who is the creditor of the company XYZ Pvt Ltd of $ 10,000. Now the company transfer the same bill of exchange to Mr P through endorsements. Thus Mr P becomes the bearer of the same BoE.
Hence on the due date (maturity date) of the bill of exchange the company ABC Ltd is obligated to pay $ 10,000 directly to Mr P, being the actual bearer of the bill of exchange.
Conclusion:
The following conclusion can be drawn from the above example.
- The company ABC Ltd (India) is the Drawer of the bill of exchange.
- The company XYZ Pvt Ltd (United States) is the Drawee of the bill of exchange.
- Mr P will be the Payee of the bill of exchange.
- The amount of bill of exchange will be $ 10,000.
- The maturity date or due date will be 90 days from the date of shipping (01/02/2020).
Hope you would have understood all about the bill of exchange. Thus we can say it plays an important role in foreign trade where the sale on credit becomes a compulsion.
You might also be interested in: