Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the Central Bank (Apex Bank) of India. RBI was established on 1st April 1935 due to enforcement of the RBI Act 1934.
Being a statutory body RBI is not only accountable for regulating the various financial institutions in India but also it performs various other functions which are explained below.
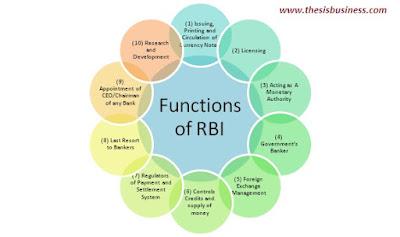
Table of Contents
(1) Issuing, Printing and Circulation of Currency Notes –
Issuing, printing and circulation of currency note are the most significant functions performed by the Reserve bank of India. It is the responsibility of a central bank / RBI to print and circulate the denominations of India.
The Reserve bank is authorised to print currency notes between only Rupees 2 to 10,000, however, for One Rupee Notes and Coins, the Ministry of Finance (Government of India) is authorised.
It is up to the RBI, what denomination is to be issued the notes between 2 to 10,000 and how to circulate the currency notes in India.
(2) Licensing:
The Reserve Bank of India is the Apex Body of different financial institutions in India. Therefore the licensing procedure of those financial institutions is under the RBI. In other words, it is the RBI who approves the license of these institutions such as:
- Commercial banks
- Cooperative banks
- NBFCs (Non-Banking Finance Company)
- MFI (Micro Finance Institutions)
- Authorised Dealers of Forex
- Recovery Agents
- ARC (Assets Reconstruction Company) etc.
(3) Act as A Monetary Authority –
RBI implements different monetary policies such as SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio), CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio), Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate to stabilize the banking system. It also decides how much money is to be circulated in the market to maintain financial stability, to stabilize the exchange rates and control inflation rate in the country.
(4) Government’s Banker –
RBI is the representative of the Government of India in the World Bank and IMF (International Monetary Fund). It is the financial advisor of the Government of India and helps in implementing various financial schemes of the Central as well as State Government.
It facilitates the government in various financial arrangements and transactions and also arranges funds through Government securities like bonds, treasury bills etc. The Reserve bank also provides short term credit to both central and state governments.
(5) Foreign Exchange Management –
RBI is authorised to regulate and monitor foreign exchange in India by FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act). It also provides guidelines regarding the balance of payment (BOP), the balance of trade (BOT), limitations of forex reserve, gold reserve.
(6) Controls Credits and supply of money:
RBI regulates and supervises the supply of money and credits as per Government guidelines. Since it directly impacts the balance of economy of a country, therefore the government has control over these phenomena through the Reserve Bank of India.
(7) Regulators of Payment and Settlement System:
RBI regulates and supervises the payment and settlement system. It works as a clearinghouse such as the settlement of ownership of clearing, NEFT, RTGS, IMPS and other electronic gateway payment mechanisms are some significant examples of the functions of RBI.
(8) Last Resort to Bankers:
The RBI is the ultimate solution for every problem of Banks in India. In case of any casualty crisis all banks approach RBI for the solution and It helps them in terms of advancing loan, repo rate and reserve repo rates etc.
RBI is also known as the Banker’s Bank as it provides loans and accepts deposits from the banks itself at the repo rate.
(9) Appointment of CEO/Chairman of any Bank:
RBI appoints the CEO/ Chairman/ CMD of whether it nationalised banks or private sector banks. In fact, the top authority of any scheduled banks can be appointed only from the final approval of RBI.
(10) Research and Development:
RBI is also responsible for surveying, research, customer satisfaction, public awareness, circulation of essential information and cautions regarding frauds in banking. It regularly performs the process of research and development to provide better banking services to consumers.