Table of Contents
Introduction –
The emergence of managerial economics has been the result of new conjunction around management and economics. Demand, benefit, expense, and competition are all concepts that involve economic analysis. In this way, managerial economics is called economics referred to as “problems of choice’’ or alternatives and distribution of scarce resources by the firms.
Economics with time has become an indispensable part of any enterprise. This single definition underpins all market expectations, forecasting, and investments.
Managerial economics is a branch of economics that incorporates managerial practice with theory. It aids in bridging the difference between logical and policy issues. The topic provides useful methods and strategies for formulating managerial policy.
Managerial Economics – Definition
Managerial economics is the application of economics to decision-making. It’s an economics division that bridges the gap between abstract theory and managerial practice. For identifying problems, organizing knowledge, and assessing alternatives, it is focused on economic analysis.
Managerial economics is goal-oriented and prescriptive by nature, with the vision of attaining optimal results. In their own terms, several economists and thinkers have provided different definitions of managerial economics.
As said by Prof. Pappas and Brigham, managerial economics is intended to include a rigorous treatment of such elements of economic theory and analysis which are most appropriate for managerial decision – making,”. Specifically, managerial economic analysis and resolution of managerial issues.
Managerial economics methods can be used to evaluate almost any business decision, but they are most widely applied to:
Risk analysis – A variety of models are used to measure risk and asymmetric details, as well as to incorporate them into risk management decision laws.
Production Analysis – Microeconomic methods are used to assess production efficiency, optimal factor allocation, expenses, economies of scale, and to estimate the firm’s cost function in production analysis.
Pricing analysis – Microeconomic methods are used to assess different pricing decisions including transfer pricing, price discrimination, price elasticity estimations, joint commodity pricing, and making a choice of the optimal pricing method.
Types of Managerial Economics –
Managerial economics is viewed differently by different managers. Customers’ experience may be a top priority for others, while others may prioritize output efficiency. As a result, various forms of managerial economics emerge. So, let’s take a look at the various approaches to managerial economics.
Liberal Managerialism –
In terms of decision-making, the market is a free and democratic environment. Customers have a variety of options to choose from. As a result, businesses must adapt their strategies to meet the needs of customers and industry dynamics. It is possible that if this is not done, the company will collapse. This is referred to as liberal management.
Normative Managerialism –
According to the normative view of managerial economics, the administration’s decisions will be natural, based on real-life experiences and practices. The choices represent a pragmatic approach to product design, forecasting, marketing, supply and demand research, hiring, and everything else related to a company’s expansion.
Radical Managerialism –
Coming up with revolutionary solutions is what radical managerialism entails. When the traditional method of solving a problem fails, radical managerialism might be the answer.
However, looking beyond necessitates the manager’s exceptional abilities and thinking. Consumer needs and satisfaction take precedence over benefit maximization in extreme managerialism.
Nature of Managerial Economics –
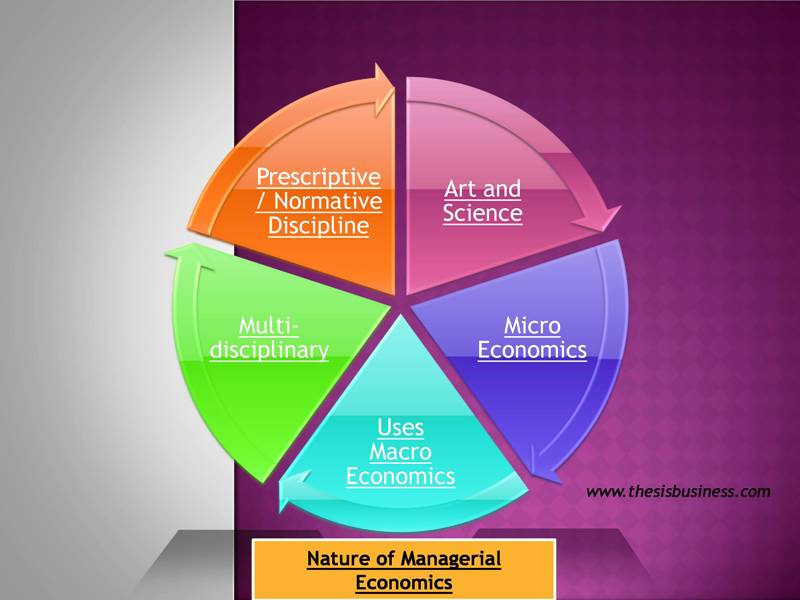
To understand managerial economics better, we must first understand its various characteristics. Take a look at the following points to learn more about the essence of this concept:
Art and Science:
For decision-making or problem-solving, managerial economics necessitates a lot of critical thought and creative skills. Some economists consider it a branch of science since it requires the application of various economic concepts, strategies, and methods to solve business problems.
Micro Economics:
Managers in managerial economics typically deal with issues specific to a single organization rather than the entire economy. As a result, it is classified as a branch of microeconomics.
Uses Macro Economics:
A business operates in an external environment, that is, it serves the consumer, which is a component of the overall economy.
As a result, managers must examine the various macroeconomic factors, such as market dynamics, economic reforms, government policies, and so on, and their effect on the organization.
Multi-disciplinary:
It employs a variety of methods and concepts from a variety of fields, including accounting, finance, statistics, mathematics, manufacturing, operations analysis, human resources, and marketing.
Prescriptive / Normative Discipline:
Its mission is to accomplish a set of objectives and to deal with real-world issues or problems by putting in place corrective steps.
Management Oriented: It serves as a tool in the hands of managers to cope appropriately with business-related challenges and uncertainties. It also enables the setting of objectives, policy development, and successful decision-making.
Scope of Managerial Economics –
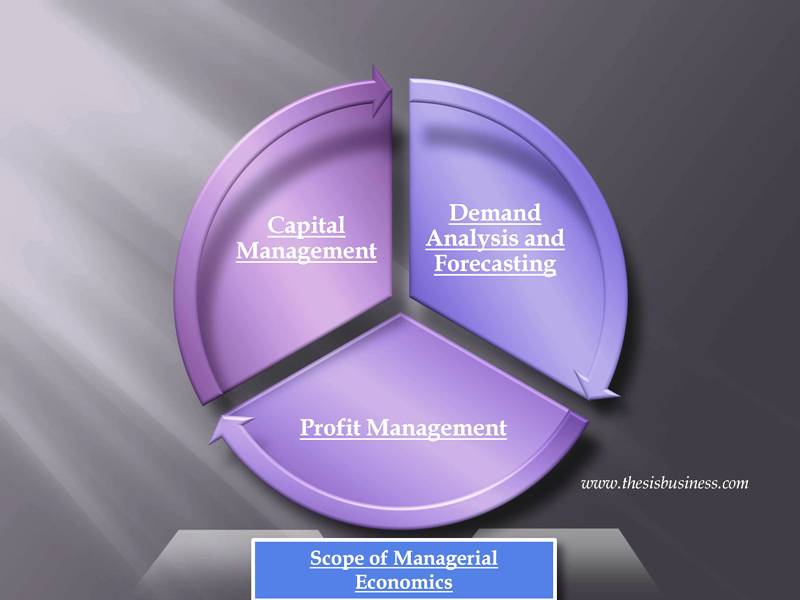
As a growing science, the field of managerial economics is always expanding. Managerial economics encompasses demand analysis and forecasting, profit management, and resource management, among other things.
Demand Analysis and Forecasting –
Demand forecasting and research necessitate a great deal of decision-making! Demand forecasting is an important part of decision-making; forecasting future revenues will help boost a company’s market position and maximize profits. Demand analysis and forecasting are extremely significant in managerial economics.
Profit Management –
Profit is the primary metric by which a company’s success is determined. Firms are run to make a long-term profit, which is usually the incentive for taking risks. The most critical and difficult aspect of managerial economics is benefit planning and measurement.
Capital Management –
Capital management entails budgeting and price transparency. There are many issues with capital projects that require a significant amount of time and effort. Capital management is influenced by the cost of capital and the rate of return.
Demand for Managerial Economics –
The increased use of economic theory, principles, tools, and hypotheses in the decision-making process of large multinationals has increased demand for this topic post-liberalization and globalization.
This can also be due to the rising demand for highly trained management staff who can optimize returns with productivity and effectiveness when working with limited resources.
Significance of Managerial Economics –
Decision-making is a challenge for management. To be manageable, decision-making requires a combination of analysis simplification and complications for dealing with a range of variables and goals. Managerial economics achieved a number of goals. It also needs common sense and sound judgment. Managerial economics can assist with decision-making in the following ways:
• Managerial economics focuses on the elements of conventional economics that are applicable to real-world business decisions. It takes ideas, principles, and techniques of analysis from economic theory and applies them to the decision-making process. These are adopted or changed as needed to allow the manager to make better decisions. As a result, administrative economics.
• If they are found to be important for decision-making, concepts from other fields such as psychology, sociology, and others are incorporated into managerial economics. In reality, managerial economics enlists the help of other academic disciplines that have an impact on a manager’s business decisions, given the various explicit and implicit constraints that must be considered when allocating resources.
• Managerial economics improves a manager’s ability to construct models. As a result, he is able to capture the basic relationship that defines a situation while overlooking the intrusive details and secondary relationships.
• At the firm level, functional specialists or functional divisions exist for different functional fields, such as finance, marketing, human resources, manufacturing, and so on. Managerial economics acts as an integrating agent, coordinating various areas and bringing the consequences of other functional areas to bear on each department’s or specialist’s decisions.
It thus facilitates business decision-making not in watertight compartments but in a holistic manner, which is important given that functional divisions or specialists often have significant autonomy and pursue competing objectives.
Conclusion –
The value of managerial economics lies in borrowing and adapting the toolkit from economic theory, integrating applicable concepts from other disciplines to make better business decisions, and acting as a catalyst in the decision-making process, by various functional divisions at the firm’s level, and eventually achieving a social goal by aligning business decisions with social responsibilities.

very good article on managerial economics .
very useful guiding principles for a managers with innovative thinking .
But lot depends on how much authority is delegated to him by higher administration.
As the responsibility and authority should go hand in hand .