In this article, we will understand the structure (or hierarchy) types of banking in India. We will also discuss the functions, importance, the purpose of establishment of each type of banks established in India. First to understand the whole topic see the following hierarchy of Banking system in India.
For the time being, let me explain the types of banking in India in this lesson. See the following structure of Indian Banking System to better understand the topic quickly.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is Central Bank of India also known as Apex Bank of India which was established on 1st Jan 1935. RBI is the supreme bank or we can say the head of all banks which is responsible for regulating and monitoring each type of banks in India.
The Reserve Bank is also responsible for implementing monetary policy, issuing currency notes, formulating various guidelines to control inflation, deflation etc.
For more details follow the link below.
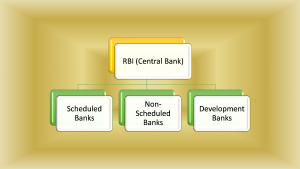
Types of Banking in India:
Basically, the Banks in India can be categorised in three segments.
- Scheduled Banks
- Non-scheduled Banks
- Development (Specialized) Banks
We will go through each segment one by one.
Scheduled Banks:
Scheduled Banks are those banks which are listed in 2nd schedule of RBI Act 1934. In other words, the banks which follow the guidelines of the 2nd schedule of RBI Act 1934. Scheduled banks can take loans from RBI at Repo rate or bank rate. Some major criteria to be scheduled banks are as follows.
- Banks must deposit 500 crores to RBI as a paid-up capital.
- Banks must open 25% of its branches in rural areas.
- At least 40% of loan must be distributed to priority sectors like SC/ST, PH, Housing, Education etc.
The scheduled banks can be further classified as follows.
1) Commercial Banks:
The Commercial Banks are those financial institutions which accept deposit and provide services like loans, credit, opening bank accounts, locker facilities, foreign exchange and other digital services like mobile banking, Internet Banking, NEFT, RTGS etc. These banks are basically profit-making and consumer-oriented institutions. In other words, these banks deal with the financial requirements of the general public.
The Commercial Bank can be classified as below.
- Public Sector Banks (PSBs)
- Private Sector Banks
- Foreign Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRB)
Let us explain each one by one in short.
Public Sector Banks (PSBs):
Those banks in which more than 50% stake is held by Government of India is defined as Public Sector Banks and the shares of these banks are listed on the stock exchange too. Few examples of banks are given below although the total number of PSBs are 27.
- State Bank of India
- Bank of India
- Punjab National Bank
- Allahabad Bank
- Central Bank of India
- Indian Bank
- Bank of Baroda
- UCO Bank
- Canara Bank
Private Sector Banks:
Private Sector banks are those banks where major stakes (51%) is of private entities. The shares of private sector banks are also listed in the stock exchange.
Few big names of private banks are below.
- HDFC Bank
- ICICI Bank
- Axis Bank
- Yes Bank
- Kotak Mahindra Bank
- IndusInd Bank
- IDFC Bank
Foreign Banks:
The banks which are incorporated or have their headquarters in a foreign country and open their branches in India as per RBI Act 1934 is known as foreign banks.
Some examples of the foreign bank are:
- City Bank
- HSBC Bank
- Standard Chartered Bank
Regional Rural Banks (RRB):
These banks are generally operating at the regional area to facilitate backward people in society. The purpose of RRBs to offer the banking services at the doorstep of rural masses especially in remote areas. These banks provide services like deposits, withdrawals, short term credit to the small farmers, labours, small entrepreneurs to increase their productivity.
2) Co-operative Banks:
The cooperative banks are a small scale banking functioning on no profit no loss basis for mutual cooperation and help. These banks generally focus on financial help for rural agriculture development. On the basis of levels of operating level, the cooperative banks are of three categories.
- State Cooperative Bank (working at State level)
- Central Cooperative Bank (working at District level)
- Primary Agricultural Credit Society (working at Rural level)
Non- scheduled Banks:
The banks which are not listed in the 2nd schedule of RBI Act 1934 is called Non-scheduled banks. These banks are not allowed to deal in foreign exchange. Basically, all commercial banks are in the list of scheduled categories. There was a bank whose name was Bank of Jammu and Kashmir was under non-scheduled category but in 2010 this also converted in a scheduled bank. Non- scheduled banks are also known as Local Area Bank although there are only four local area
banks in India which are as follows.
Coastal local area Bank ltd:
This Vijaywada, Andhra Pradesh based bank was established on 27 Dec 1999 and operating in Krishana, Guntur and West Godavari.
Capital local area bank ltd:
This bank was established on 14 Jan 2000 and operating in Jalandhar, Kapoorthala and Hoshiarpur in Punjab.
Krishana Bhima Samuriddhi Local area bank ltd:
This bank was established on 28 Feb 2001 and based at Mahboobnagar, Andhra Pradesh. The area of operations is Mahboobnagar in Andhra Pradesh and Raichur, Gulbarga in the State of Karnataka.
Subhadra Local area bank ltd:
This bank is based at Kolhapur having only 8 branches.
3) Development Banks:
The development banks were established for the purpose of development of different sectors like agriculture, housing, small industry and foreign trade. These banks don’t deal in public. Following are the list of development banks.
This was the first Development Bank of India which was established in 1948 by the Government of India. The headquarters of IFCI is situated in New Delhi. The main purpose of this bank was to provide long term finance to the industrials.
NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development):
This bank was established on 12 July 1981 by the recommendation of B. Shivaraman Committee being headquartered in Mumbai. The initial capital of this bank was 100 crores later RBI sold its stakes to Government of India which holds 99% stakes of NABARD now.
NABARD was established especially for the development of agriculture and rural area and handle financial problems mainly related to agricultural and rural development.
EXIM BANK (Export-Import Bank):
This bank was established to encourage foreign trade of India. Its main objective is to arrange funds for the companies which are dealing in export-import business. This is fully owned bank of Government of India and established under Export-Import Bank of India Act 1982.
NHB (National Housing Bank):
This bank was established on 9 July 1988 by the Government of India. This bank is regulated under the National Housing Bank Act 1988 and also is the supreme bank of the housing and finance.
The main objective behind setting up this bank was to make available easy and affordable housing loans at the regional and local level.
NHB is also responsible for regulating activities of the housing finance companies in India.
SIDBI (Small Industries Development Bank of India):
SIDBI was established on 2nd April 1990 under the Small Industries Development Bank of India Act 1990 having its headquarter in Lucknow (UP). SIDBI was set up for the promotion, financing and development of small, micro, medium industry in India.
Moreover, the objective of SIDBI is to strengthen and facilitates entrepreneurs who are facing financial problems in expanding their businesses.
MUDRA Bank (Micro Unit Development and Refinance Agency Bank):-
MUDRA Bank was established on 8 April 2015 and launched by the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi with the initial capital of 2000 crores and a credit guarantee fund of 3000 crores under Pradhan Mantri MUDRA scheme.
Initially, this bank is functioning as Non- financial company and subsidiary of SIDBI. Later on, this will be made a separate institution.
The principal objective of this bank to provide loans to small manufacturing unit, shopkeepers and street vendors at low-interest rates under the following schemes.
- Shishu (up to 50,000)
- Kishore (up to 5 lakh)
- Tarun (up to 10 lakh)
Conclusion:
Hope this article would be able to guide you to understand the types and structure of the Indian banking system. In a nutshell, there are three major types of banks in India: Commercial banks, cooperative banks and development banks. The Reserve Bank is the head of all types of banks operating in India, that means every bank has to follow the rule and regulation of RBI.
You may also interested in,
Nationalisation of Banks in India